Hardware Components. Central Processing Unit
The CPU, known as the Central Processing Unit or processor, serves as the computer system’s primary controller. It is the primary hardware element that carries out commands. These operations may involve arithmetic calculations or logical comparisons.
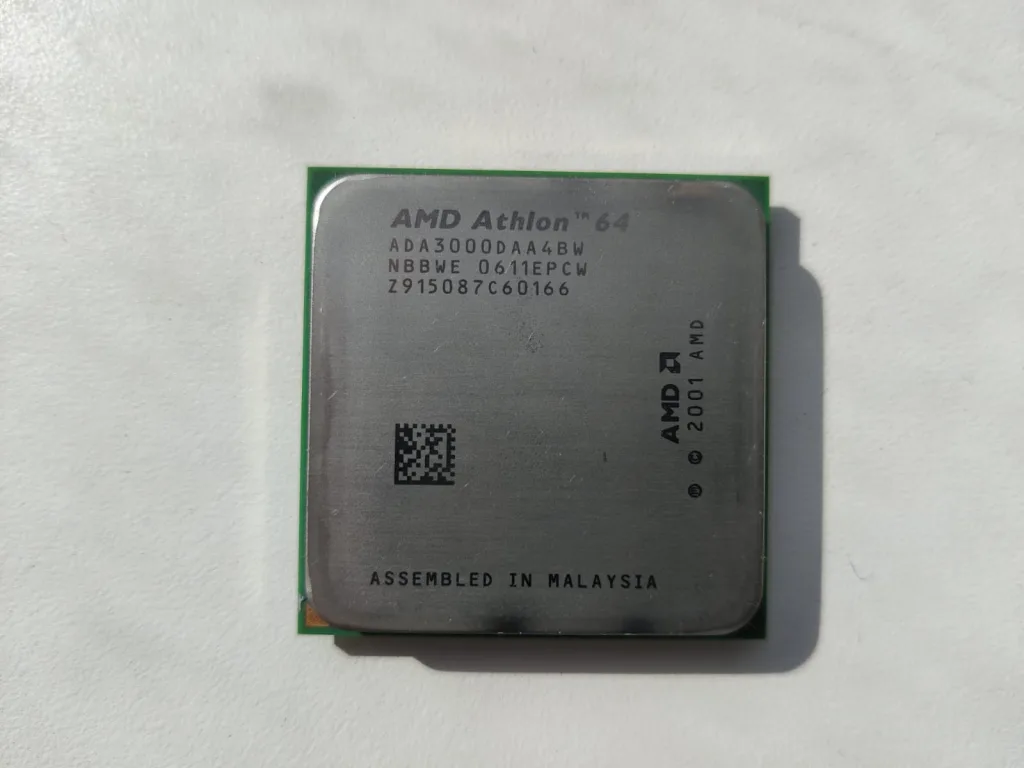

AMD Athlon 64 CPU
The CPU receives instructions and data from the primary memory (RAM) and executes them. I/O commands, that refers to the Input/Output communication among the computer system and external devices (like keyboards, monitors, storage drives, etc.), are not used directly; they are managed by other components that interact with the CPU. The CPU functions as the primary component that determines the system’s processing power and speed.

Pins on the back of a CPU
Essential CPU Features
Instruction Set Architecture (ISA):
- x86 (Intel and AMD): Dominant, CISC (Complex Instruction Set Computing), architecture for desktops and laptops, capable of handling both 32-bit (x86) and 64-bit (x86_64) instructions. Offers complex instruction set for performance but can be power-hungry.
- ARM: RISC (Reduced Instruction Set Computing) architecture is famous for being efficient and having low power consumption, making it perfect for mobile devices. Employs a less complicated set of instructions in comparison to x86.
- PowerPC: Another RISC structure utilized in servers and embedded systems, appreciated for its dependability and processing in real-time.
Processing Power:
- Core Count: Contemporary central processing units frequently contain numerous processing cores (each functioning as a miniature processor) on a solitary chip, allowing them to manage numerous tasks at the same time.
- Clock Speed: Measured in gigahertz (GHz), the frequency represents how many operations the CPU can carry out within each second. Typically, faster performance is achieved with higher clock speeds, although core count and architecture are additional factors that contribute to overall speed.
Memory Management:
- Cache Memory: A small cache of high-speed memory on the CPU that holds commonly used data and instructions. Increased cache sizes enhance performance by minimizing the necessity of accessing slower main memory (RAM).
Additional Features:
- Integrated Technologies: Current CPUs frequently come with added functionalities such as hardware virtualization technologies (for example, Intel VT-x, AMD-V) that enhance overall performance when operating virtual machines.
Fabrication process:
- Referred to as process node or nanometer (nm) technology: An important element impacting the performance, power efficiency, and density of transistors in CPUs. It basically determines the dimensions of transistors, which are essential components of a CPU.