Hardware components. Motherboard
Hardware is made up of physical components that make up a computer system. Normally, hardware is comprised of electronic components contained within a casing. Usually, systems follow a conventional layout containing various shared components that work together through interfaces.
Motherboard
The motherboard serves as the main hub, connecting all the necessary components of a computer system with its circuitry. It contains the CPU socket which determines the type of processor that can be used. It also sets the limit for the system’s RAM capacity and provides different connection possibilities for expansion cards (PCI, PCI-X, AGP, PCIe), storage devices, and peripheral management overseen by the southbridge chipset.
This basic feature set includes crucial elements such as RAM slots, motherboard power connectors, and a CMOS battery for preserving BIOS configurations. Headers are included to link front panel functions such as power buttons, LEDs, and USB ports.
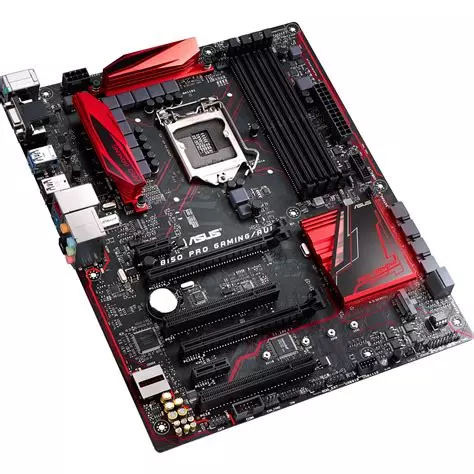

ASUS B150 PRO GAMING/AURA Motherboard
Contemporary motherboards have the capability to include extra features such as a Network Interface Card (NIC) for wired internet access, a Wi-Fi card for wireless connections, or a sound card for audio manipulation. Headers could offer extra USB ports, SATA ports, or Thunderbolt ports for fast devices.
Regarding storage, the motherboard provides connections for additional options other than those initially stated. Common options consist of SATA, which is the prevailing interface for both hard disk drives (HDDs) and solid-state drives (SSDs). PATA, which is also recognized as IDE, is a previous standard that may be found on certain systems.

SanDisk 1TB 3D SATA III 2.5″ Internal SSD
Modern motherboards now have the ability to utilize NVMe, a high-speed storage solution that takes advantage of the PCI Express bus for extremely fast data transfer rates, for advanced performance. M.2 is a design for storage devices that can support either SATA or NVMe technology.
Although the northbridge chipset used to connect the CPU, memory, and graphics card in older motherboards, newer motherboards integrate the northbridge into the CPU. Furthermore, the motherboard can also integrate different components such as the network card and RAID (Redundant Array of Independent Disks) controllers. Nonetheless, they have the potential to function as individual parts that link up via expansion slots.
Recognizing the significant difference between motherboards for desktops and servers is crucial. Some features that servers can have include:
- Hot-swappable technology allows for memory modules, hard drives, and occasionally power supplies in servers to be replaced while the system is still operational.
- Servers can support multiple central processing units for enhanced processing power and scalability.
- Sophisticated RAID controllers are commonly integrated in servers to improve data protection and redundancy through Redundant Array of Independent Disks technology.
- Servers often come with multiple network cards for increased reliability and better network speed. This enables a backup in case one card fails or spreads network traffic over different connections.
- Improved cooling: servers come with efficient cooling systems to handle the excess heat generated by their powerful parts. This may include characteristics like larger fans, heat pipes, and specific airflow routes.